| Conventional Bike Lane |
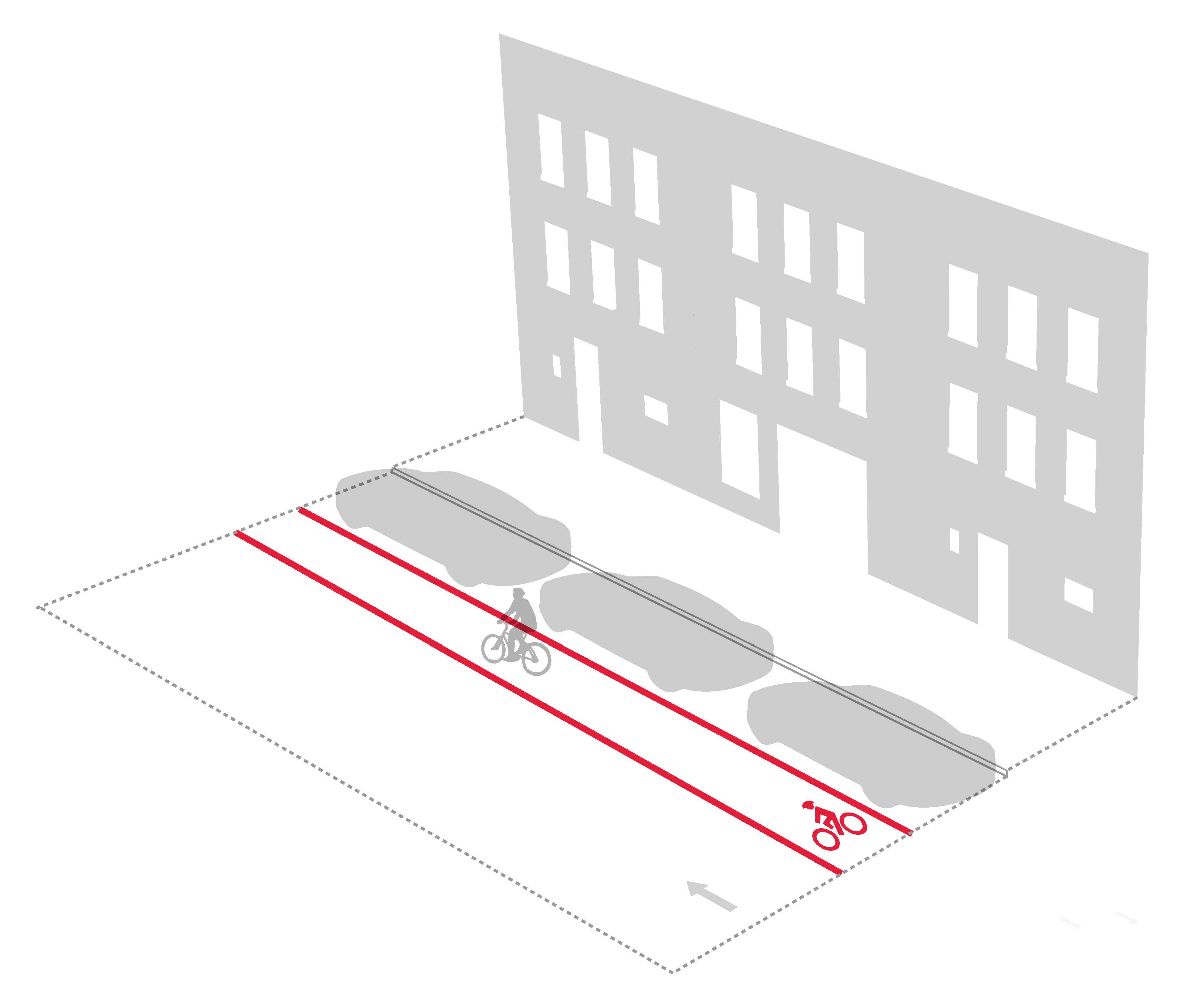 |
5–6’ standard |
• One- or two-lane street
• Excess road space
• Low potential for intrusion into bike lane |
• Dedicated roadway space for cycling
• Preserves curbside access
• Simple implementation |
• Vehicular intrusion possible
• Minimal separation from traffic
• Perceived as less safe than protected lanes |
Standard if lane is adjacent to curb or between travel and turn lane (“pocket lane”) |
| Shared Lane |
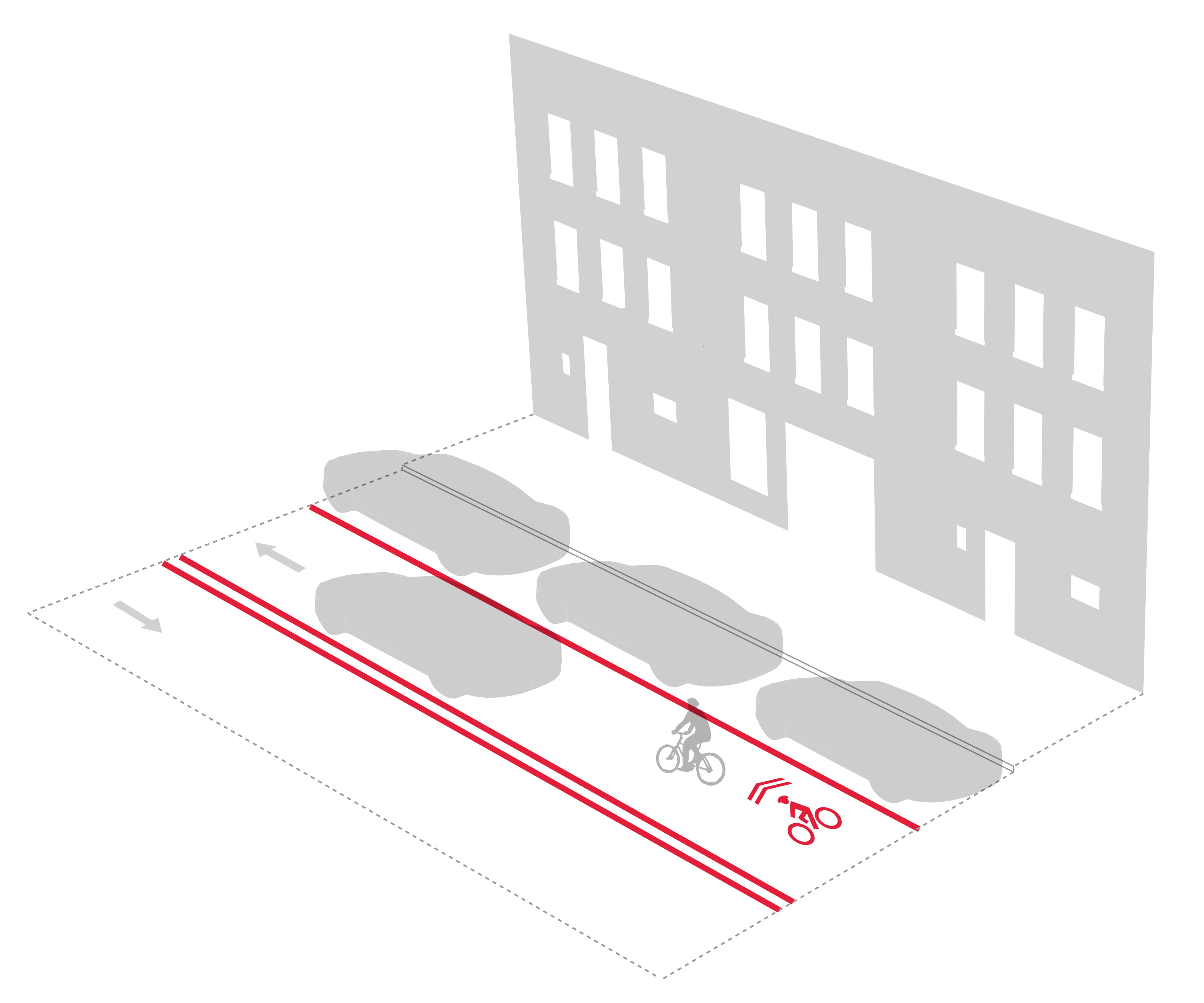 |
None |
• One- or two-lane street
• No excess road space
• Connected to other bike facilities |
• Easy to follow bike route
• Heightens driver awareness of cyclists
• Preserves curbside access
• Simple implementation |
• No dedicated space for cycling
• Cyclists not separated from traffic |
Chevrons to indicate bike facility |
| One-Way Protected Bike Lane |
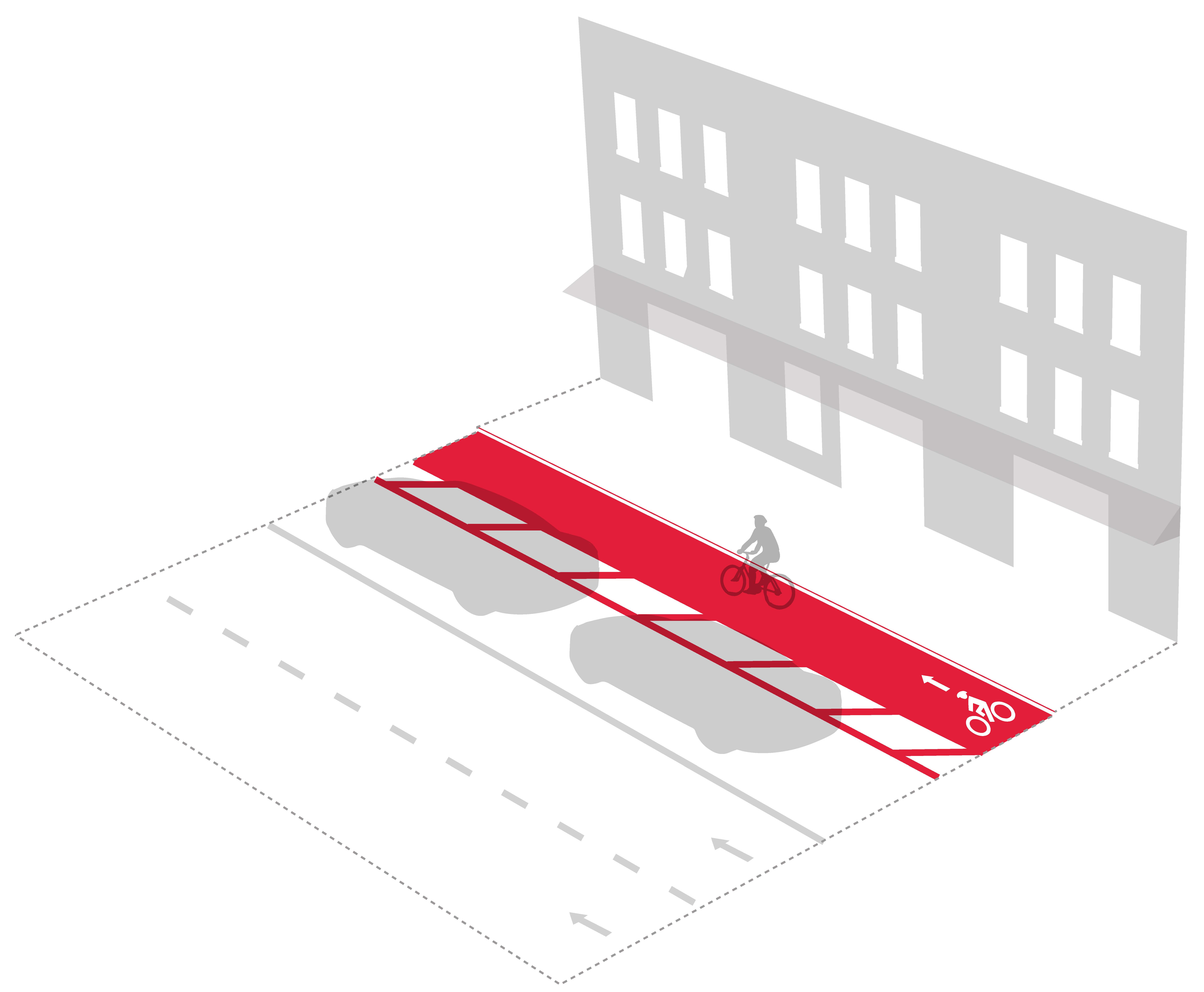 |
4’ min. lane + 3’ min. buffer (4’ min. buffer if no maintenance plan) |
• Excess road space
• Low-speed vehicular traffic
• High potential for bike lane intrusion |
• Protected space for cyclists
• Safety benefits for all modes
• Allows pedestrian improvements like safety islands |
• Parking/loading impacts
• Complex to regulate floating parking
• Signal timing issues
• Maintenance plans required at safety islands |
Standard if parking turnover is high |
| Two-Way Protected Bike Lane |
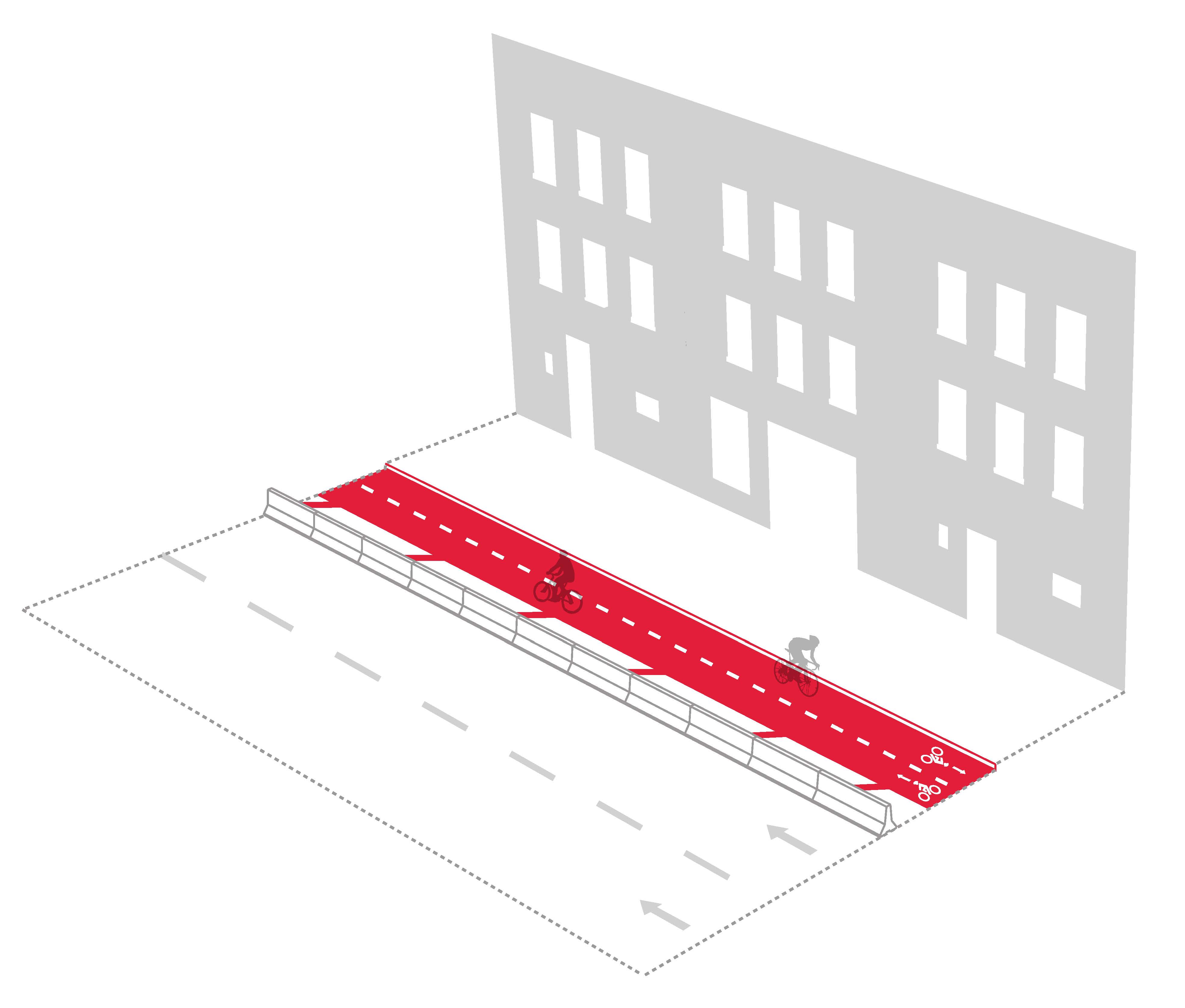 |
8’ min. (4’ per lane) + 3’ buffer (2’ if Jersey barrier used) |
• Favorable edge conditions
• Excess road space
• Adjacent to parks/waterfront
• Within industrial areas |
• Efficient use of space
• Enhanced visibility
• Safer passing for varying cyclist speeds |
• Parking impacts
• Signal timing and turn control needs
• Complex implementation |
Preferred if exclusive to cyclists or in high pedestrian volume areas |
| Grade-Separated Bike Lane |
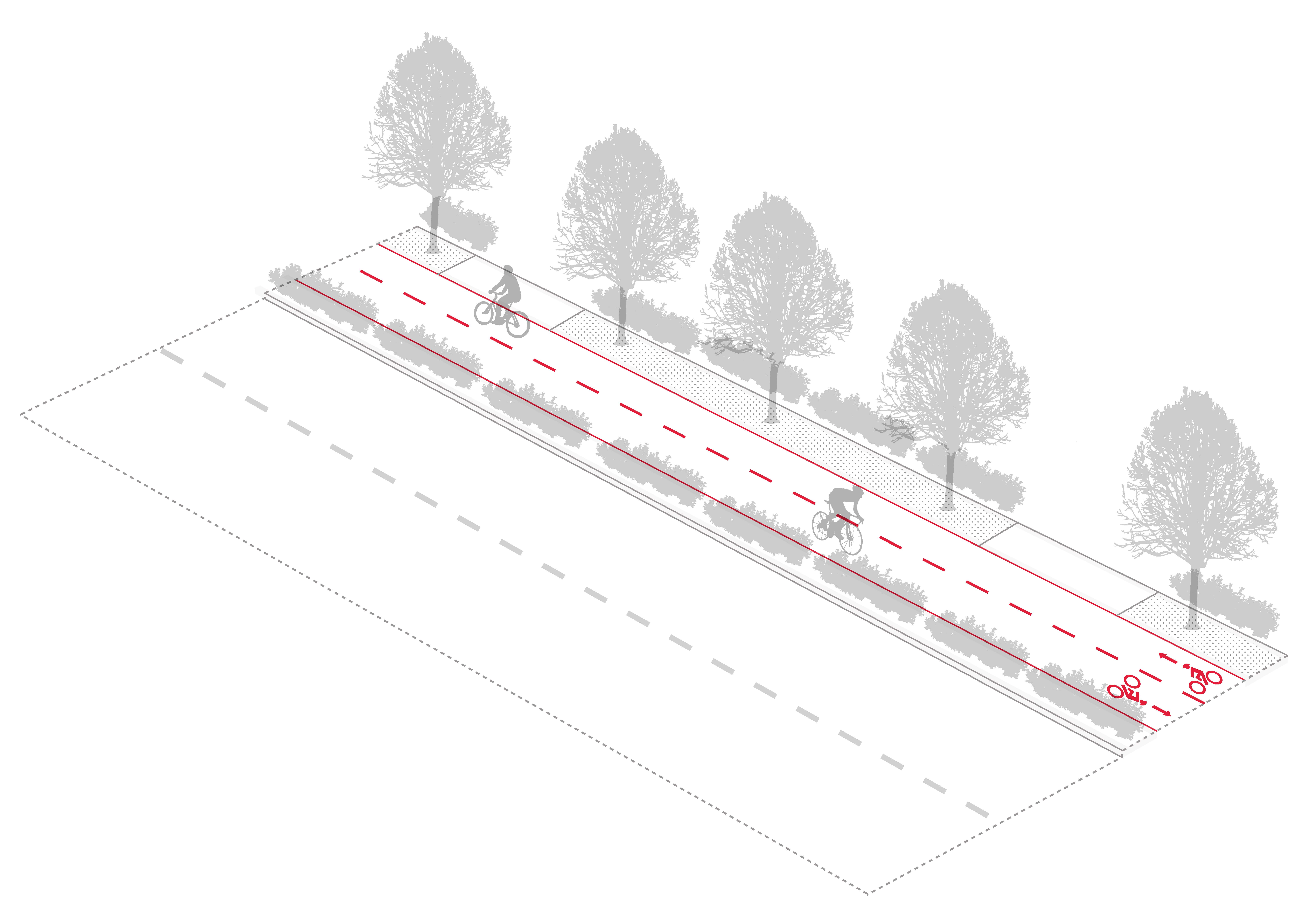 |
5’ min. one-way, 8’ min. two-way + buffer |
• Greenway segments
• Through parks/waterfront spaces |
• Greatest safety benefit
• Connects inaccessible segments
• Preserves curbside access |
• Often requires capital work
• Complex implementation |
Not used with continuous vertical protection |